Climate science shows that in order to halt or slow climate change, carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions must stop. ‘Net zero’ means that any emissions are balanced by absorbing an equivalent amount of carbon from the atmosphere. Transport accounts for around one-quarter of global carbon emissions from energy. In richer countries like the UK with populations that travel often, transport can be one of the largest segments of an individual’s carbon footprint.
Transition Bath – following the principles of the Transition Network – believes local transport policies and plans should commit to a target of zero carbon in response to the worsening climate emergency. We also want to take into account that the climate crisis is impacting less advantaged people more and posing an irreversible threat to the ecological systems upon which human life depends.
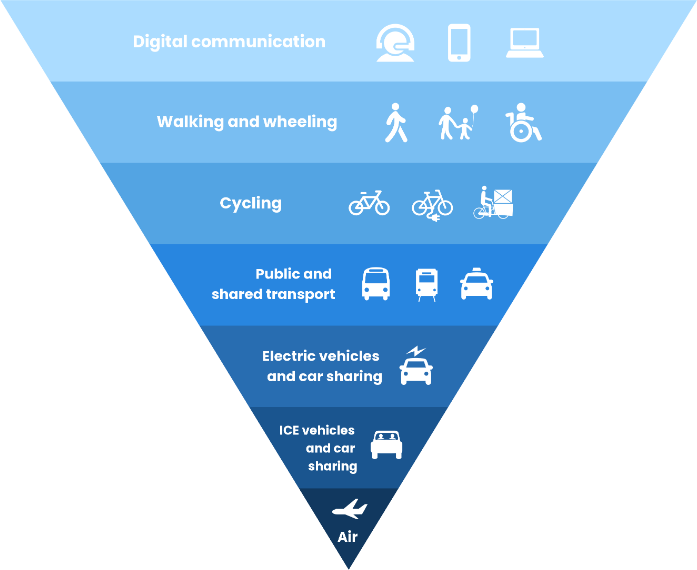
Sustainable Travel Hierarchy
The sustainable travel hierarchy is a useful tool to help you think about improving the impact of your journeys. In order to reduce their carbon footprint, everyone needs to do what they can to move up the sustainable travel hierarchy, The higher up the hierarchy, the more sustainable and greener the travel option. Note that some scientific research concludes that cycling has a lower carbon footprint than walking, or a similar footprint.
The travel hierarchy is as follows, ranging from most sustainable to least sustainable:–
- Digital communication
- Walking and wheeling
- Cycling
- Public and shared transport
- Electric vehicles and car sharing
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicles and car sharing
- Air
Furthermore, as its population increases, Bath and its surrounding areas cannot sustain existing modes of low-capacity transport without considerable effect on air pollution and congestion. Overall this means we need to make more use of our transport highways by more sustainable modes of transport.
How to support change
Transition Bath believes that any changes to our transport system and the way in which we use it needs to encompass the following: